Some web design tips are supported by actual brain science. Research into the brain reveals tendencies. These tendencies translate into tips for designing websites. In fact, specific parts of the brain relate to specific marketing methods.
The Frontal Lobe (planning, logic, motivation)
The frontal lobe is associated with “executive functions” such as motivation, planning, attention, and short-term memory. It considers options and the consequences of actions.
1. List Order and “Serial Position Effect”
When ordering your navigation (or any lists within your copy), put the important stuff at the beginning and end. The readers’ attention and retention are lowest in the middle. As visitors scan the page, the first and the last items are most likely to stay in short-term memory. [1]
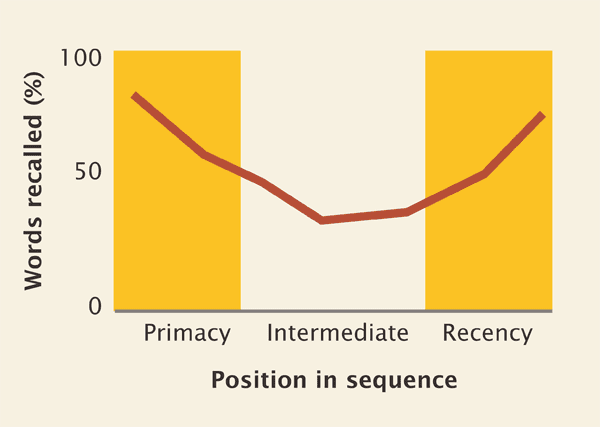
Also, don’t include too many items. Short term memory can only hold around seven items. If your navigation includes more than seven links, break it up into smaller groups.
2. Marketing Copy and “Loss Aversion”
Humans are not efficient cost/benefit calculators. We tend to overvalue losses and undervalue gains. In other words, losses are more painful than gains are pleasurable.
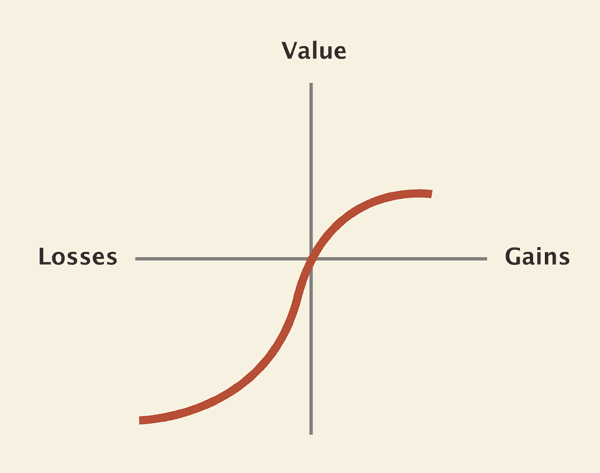
This aversion to losses can be useful to web designers and copywriters. Here are some tips for writing copy with loss aversion in mind. [2]
- Emphasize the costs of not using your product or service.
- Group costs together, list benefits separately.
- Emphasize immediate gains.
- Create urgency with limited time offers. If the product is scarce, say so.
3. Social Proof and Supportive Content: Herd Behavior
People tend to do what other people are doing. So giving evidence that others have selected you makes choosing your company seem like a good choice. The goal is to make any decision other than using your company seem outside the norm.
Add supportive messages:
- Testimonials from clients or reviews from customers
- Social media widgets showing the size of your following
- Endorsements from relevant influencers
- “As seen in…” logos of media where your company has been mentioned
- Trust seals, including association memberships, security certificates, and awards
These elements improve the initial value judgement of your website and your company.
Temporal Lobe (language)
Together with the frontal lobe, the temporal lobe plays a key role in language comprehension. This is where language and meaning is processed.
4. Word Choice and Readability
Labels in navigation and copy in pages must be easy for visitors to understand. Use the common words that visitors expect. Avoid long sentences. Don’t use jargon. Long sentences and fancy words force the temporal lobe to work harder. Not good.
Copy that works well for “low literacy” users works well for everyone. It’s not about dumbing it down; it’s about using simple language that everyone can understand. Even PhDs prefer to read at an 8th grade level. [3]
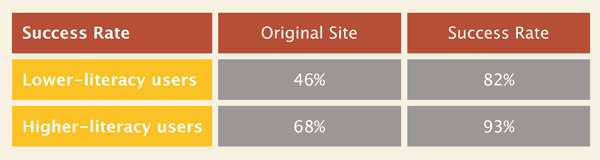
A big word might make you sound smart, but it risks making the reader feel dumb. A reader who doubts themselves is unlikely to take action. And you want to inspire action, right? Be simple and accessible in your writing.
Occipital Lobe (vision)
This is the visual processor of the brain, handling spatial, color, and motion perception.
5. Colors and “Von Restorff Effect”
In the 1930’s, German scientist Hedwig von Restorff discovered that when given a list of ten items, people remember items if they are a color different from the others. This is because the occipital lobe is sensitive to visual differences, or “pattern interrupters.”
Web marketer, Paras Chopra, conducted experiments that showed how standout colors aren’t just remembered more, they’re clicked more: 60% more! [4]
Pick an “action color” for all of your links, buttons, and rollover effects. Make it a color that’s distinct from the brand colors used throughout the design (these are the “passive colors”). Use the action color nowhere else but in the clickable items.
Amygdala (basic emotions)
The amygdalae (there are two) are key in the formation and storage of emotional memories.
6. Headlines: Emotion and Virality
According to eye tracking studies, headlines aren’t just the first thing seen on a page, they’re looked at more than anything else. [5] And not all headlines get shared equally.
Headlines and images can quickly spark emotions. Research shows that emotional headlines get shared more. [6] A lot more. The three types of emotions that get shared the most: anxiety, anger, and inspiration.
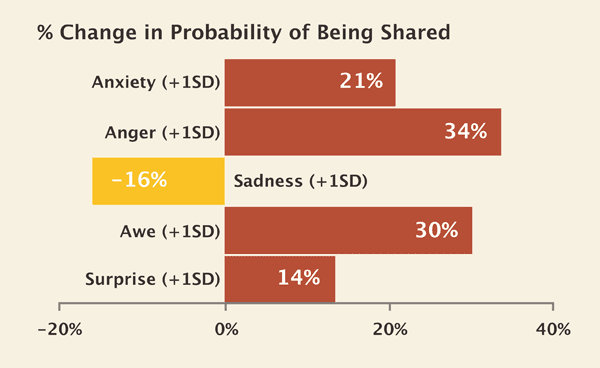
Especially for blog posts, write headlines that trigger very positive (or very negative) emotions. In the words of Antonio Damasio, “We are not thinking machines that feel, we are feeling machines that think.”
Results May Vary
Web marketing is a science, and science is about testing. Try these techniques in your web design and web marketing, and measure the results. You may find that some tips work better than others. But any technique that takes brain anatomy into account is likely to work well!
Sources:
- [1] Order Effects Theory: Primacy versus Recency
- [2] Applying Behavioral Economics And Cognitive Psychology to the Design Process
- [3] Lower-Literacy Users: Writing for a Broad Consumer Audience
- [4] Multivariate Testing in Action: 5 Simple Steps to Improving Conversion Rates
- [5] Eyetrack III
- [6] What makes online content go viral?
Comments